Slot Antenna For Microwave Ablation
- Coaxial Slot Antenna For Microwave Ablation
- Slot Antenna For Microwave Ablation Instructions
- Slot Antenna For Microwave Ablation Surgery
- Slot Antenna For Microwave Ablation Without
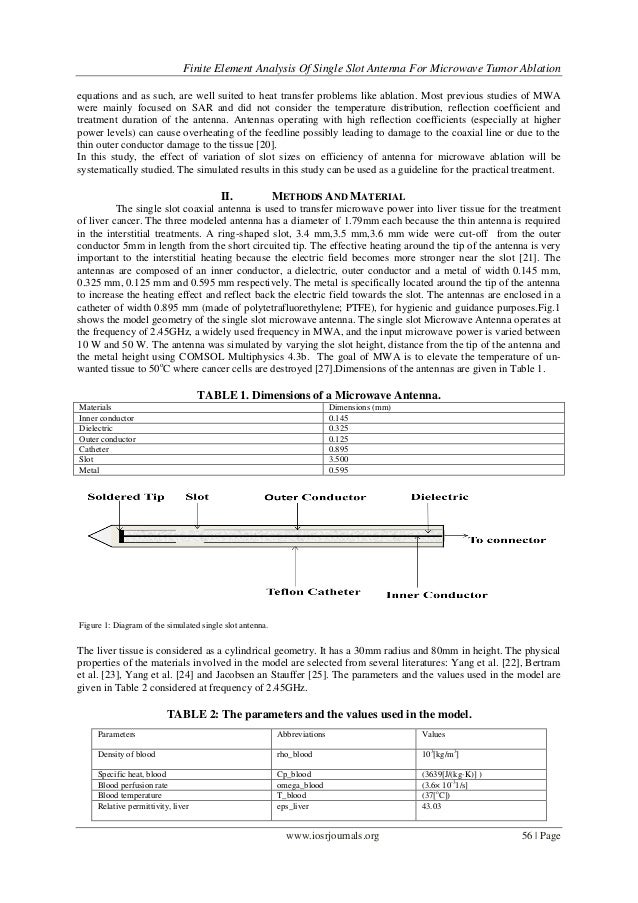
Axial and radial schematics of a coaxial-based double slot choked antenna designed for hepatic microwave ablation (MWA). All units are in mm. Where c is the speed of light in free space (m/s), f is the operating frequency of the microwave generator (2.45 GHz), and ε r = 44.4 is the relative permittivity of bovine liver tissue at the operating frequency; this yielded 18.4 mm for the effective wavelength. Microwave ablation is a minimally invasive surgical technique for the treatment of primary and secondary liver tumors. After localizing the tumor with imaging guidance, a thin microwave antenna is placed directly into the tumor. A microwave generates electromagnetic waves that heat water molecules. In this study, a thin coaxial antenna for microwave ablation (MWA) is proposed. A helical slot is added between two slots in order to overcome the disadvantage of the radiation range extending to.
- Microwave energy is a promising alternative treatment because it can preferentially heat and damage high-water-content breast carcinomas. In order to evaluate the feasibility of using this technique to treat breast cancer, a coaxial slot antenna computer simulation based on an axisymmetric finite element method (FEM) model was used to compare.
- We optimized dual slot antenna for microwave ablation by adding metallic sleeve. Low backward heating along antenna shaft is possible by adding metallic sleeve. Metallic sleeve on the designed antenna helps to create higher ablation sphericity.
- We optimized dual slot antenna for microwave ablation by adding metallic sleeve. Low backward heating along antenna shaft is possible by adding metallic sleeve. Metallic sleeve on the designed antenna helps to create higher ablation sphericity. Specific absorption rate was localized by the presence of metallic sleeve on the antenna.
- Investigation of the structures and properties of antennas is important in the design of microwave ablation (MWA) system. In this study, we studied the performance of the novel tri- and single-slot antennas with frequency of 433 MHz in ex vivo conditions.
Abstract
Coaxial Slot Antenna For Microwave Ablation
Microwave ablation is a technique used in treating hepatocellular carcinoma, especially in cases where surgical removal is impossible. In the present study we are investigating the effects of design characteristics of a coaxial slot antenna (single- versus double-slot, slot-to-tip distance and slot size) on the ablation zone characteristics (dimensions and shape). The specific absorption rate field and the temperature rises are calculated for a variety of application times and powers. A plateau in the ablation zone dimensions in healthy and cirrhotic liver models is predicted, but not in malignant ones. It is found that the value of the perfusion rate (which is different for each clinical case) is of crucial importance in order to correctly estimate the ablation zone. An underestimation of dimensions is expected, if higher perfusion rates are used (i.e., values for healthy tissue rather than malignant). In contrast, an exact determination of the values of relative permittivity and conductivity is less significant for predicting the ablation zone.
'Cache Creek Bill Progresses Despite Opposition'. Friends of the River (Spring 2005): 14.References. Graton casino rohnert park ca.
Export citation and abstract
Slot Antenna For Microwave Ablation Instructions
General scientific summary Microwave ablation (MWA) is a novel, minimally invasive, thermal-based technique used in treating hepatocellular carcinoma. In this study we present clinically relevant numerical models, aimed to quantify the characteristics (dimensions and shape) of the ablation zones. Such information can aid in patient-specific pre-treatment planning. Coaxial antennas of different designs (single- vs double-slot, various slot-to-tip distances and slot sizes) were modelled and their performance was compared. Double-slot antennas in the range of about 10 mm were found efficient. Regarding modelling the tissue, we showed that the value of perfusion rate (which is different for each clinical case) determines the behaviour of the ablation zone. Its correct evaluation is of crucial importance to estimate the extent of heating. As a step to close the gap between experimental and theoretical studies, we showed that an underestimation of dimensions is expected when higher perfusion rates (as such of healthy rather than malignant liver) are considered.
Access this article
Login options
Individual loginorInstitutional login
via Athens/ShibbolethorIPEM member access
The computer you are using is not registered by an institution with a subscription to this article. Please log in below. Find out more about journal subscriptions at your site.
Rent or Purchase this article online
Make a recommendation
Slot Antenna For Microwave Ablation Surgery
To gain access to this content, please complete the Recommendation Form and we will follow up with your librarian or Institution on your behalf.
For corporate researchers we can also follow up directly with your R&D manager, or the information management contact at your company.
Slot Antenna For Microwave Ablation Without
Institutional subscribers have access to the current volume, plus a 10-year back file (where available).